Curcumin and its Role in Menopause
- Sharad Jaiswal
- Jul 15, 2024
- 6 min read
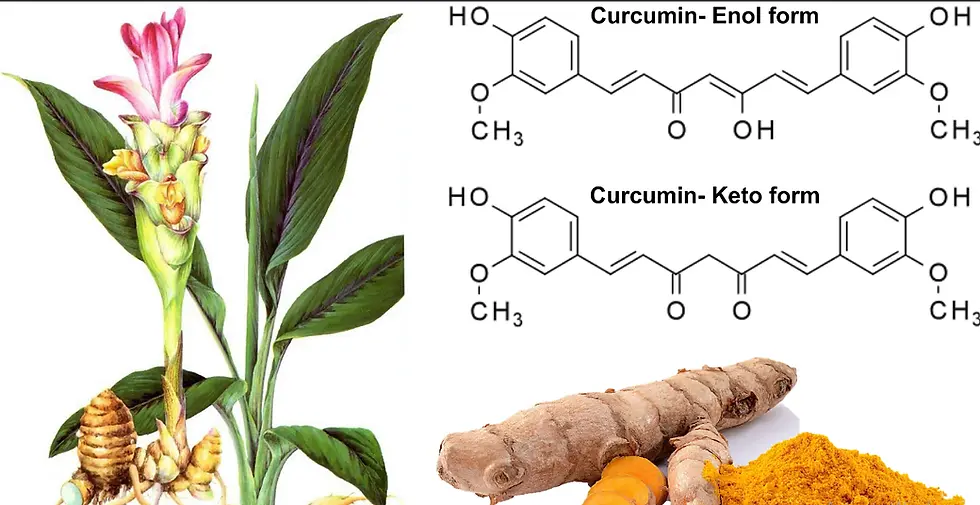
Curcumin
Curcumin is an organic compound found in spice turmeric, which is often used in Indian cuisine.
The polyphenolic component, which gives the spice its distinctive color and has been associated with many health benefits, is to blame.
Curcumin is a member of the curcuminoid family of chemicals, which possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Numerous biological benefits have been identified, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and neuroprotective properties [1].
Among the many molecular targets, it may interact with within the body are enzymes, transcription factors, and cell signaling molecules.
Due to its adaptability and ability to have a variety of biological effects, curcumin is a very alluring pharmaceutical prospect. The second is the favorable health effects of curcumin. Among the conditions that curcumin may treat include inflammation, brain function, and heart health.
Diabetes, cancer, and heart disease are just a few of the chronic diseases that are significantly impacted by chronic inflammation.
Curcumin has been shown to have neuroprotective properties that may help slow down or prevent cognitive decline. • It has been shown that BDNF, a protein crucial for the growth and survival of neurons, may be produced more abundantly. • Curcumin reduces inflammation throughout the body by blocking the activity of many pro-inflammatory chemicals.
Given that low levels of BDNF have been linked to a variety of neurological conditions, such as depression and Alzheimer's disease, this discovery is very significant.
Studies have demonstrated that curcumin has several positive effects on heart health.
A particularly promising natural substance that may provide numerous health advantages is curcumin. Due to its distinctive chemical structure, it can interact with a variety of biological targets and possibly have a wide range of advantageous effects [2].
Menopause and its Risk Factors
All women experience menopause at some point in their lives as part of the normal ageing process. It is the stage of life when menstruation ends permanently.
The hormones that control the menstrual cycle, estrogen and progesterone, are in decline throughout menopause.
It may take several years for hormone levels to fully drop, which happens gradually over time.

A woman's life is significantly affected by menopause.
The loss of ovarian function after menopause is one of the most important biological variables.
For the female reproductive system to work properly, estrogen must be produced by the ovaries [3].
During menopause, the body goes through many changes when the estrogen level falls.
Hot flashes, mood fluctuations, decreased sex drive, and vaginal dryness are a few of these changes.
Menopause risk factors include genetics, lifestyle, and past reproductive history. Early menopause is more likely in women who smoke, have bad eating and lifestyle habits, and have a history of the condition in their families.
Early menopause may also occur in women who have undergone specific medical operations, such as a hysterectomy or radiation therapy.
Hormone replacement therapy, non-hormonal therapies, and lifestyle modifications are all possible menopause treatments.
In hormone replacement treatment, estrogen and progesterone are added to the body's natural amounts of each hormone. Hot flashes and vaginal dryness are two menopause symptoms that can be helped by this treatment.
However, because hormone replacement therapy has been associated with an elevated risk of breast cancer, women must consider the advantages and dangers of this treatment with their healthcare professionals.
Drugs like antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and blood pressure drugs are examples of non-hormonal therapy. These drugs can aid in controlling menopausal symptoms like hot flashes and mood swings [4].
Menopause symptoms may also be reduced by modifying one's lifestyle through activities including consistent exercise, a balanced diet, and stress reduction techniques.
In conclusion, all women go through menopause at some point in their life. It is a natural process.
There are numerous therapy options available to assist control symptoms and enhancing the quality of life, even though it may be a difficult period for some.
Women must investigate all therapy choices and discuss their menopause symptoms with their healthcare professionals to find the best course of action for their particular requirements.
Curcumin and its Role in Menopause
It has been demonstrated that the turmeric ingredient curcumin, a natural phytoestrogen, has advantageous effects on menopause.
Menopause, which signifies the end of a woman's reproductive years and is characterized by a sequence of hormonal fluctuations and many unfavorable symptoms, is a normal physiological process.
Women's quality of life is impacted by these symptoms, which also have an impact on their physical, emotional, and mental health. Menopausal symptoms are frequently treated with hormonal therapy, although this has a lot of drawbacks.
Therefore, natural substances with strong biological activities that can be utilized as an alternative to hormone therapy, such as curcumin, are of interest to researchers.
Curcumin is a promising phytoestrogen treatment for menopause because have both estrogenic and anti-estrogenic effects [5].
Curcumin interacts with estrogen receptors, which are typically present in estrogen-sensitive tissues like the breast, bone, and uterus, as a result of its estrogenic qualities.
Contrarily, curcumin's anti-estrogenic qualities allow it to control the body's estrogen levels. Due to its dual effects, curcumin helps to alleviate menopause like mood swings and hot flashes.
Curcumin's capacity to regulate estrogen production throughout menopause is one of its many noteworthy advantages.
The enzyme aromatase, which turns testosterone into estrogen, is inhibited by curcumin, causing estrogen levels to drop.
According to studies, estrogen dominance—which is linked to higher levels of aromatase in menopausal women than in premenopausal women—contributes to menopausal symptoms.
As a result of curcumin's inhibition of aromatase, the body's estrogen levels are regulated, alleviating menopausal symptoms.
Curcumin is a useful treatment for menopause since it has strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects [6].
By preventing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which cause inflammation-related symptoms like joint pain, night sweats, and hot flashes, it lowers inflammation.
Curcumin can lessen the severity and frequency of these symptoms, offering relief to women who experience them and improving the quality of life for menopausal women.
It has been demonstrated that menopausal women may benefit from it. It can be useful in the following ways:
Curcumin may help lessen the frequency and intensity of hot flashes, a common menopause symptom, according to research
Studies have shown that curcumin has antidepressant properties, which may help women dealing with mood swings throughout menopause.
Curcumin, a strong anti-inflammatory compound, can help relieve menopausal women's symptoms like joint pain and stiffness.
Studies have shown that curcumin can aid in boosting bone density and reducing bone loss. This is particularly advantageous for women going through menopause, a time when bone health is frequently a worry.
Given its powerful estrogenic and anti-inflammatory characteristics, curcumin is a viable natural therapy for menopause.
It works well in place of hormonal therapy since it controls estrogen levels and lowers inflammation. Curcumin can help menopausal women by reducing their symptoms and improving their quality of life [7].
Future research will help to improve curcumin use as an alternative treatment for menopause by determining its dosage, safety, and efficacy in this condition.
Pre-Clinical and Clinical Trial Data
Clinical and human trials have been conducted to determine whether curcumin is effective at treating the symptoms of menopause.
The anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer effects of curcumin are known. Due to these qualities, curcumin has emerged as a potential treatment for menopause-related illnesses like osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease.
Postmenopausal women were given curcuminoids for eight weeks during one research experiment.
The curcuminoids considerably enhanced bone microarchitecture, decreased bone loss and raised bone density [8].
Curcumin has been looked at as a possible treatment for menopausal symptoms in many clinical investigations.
According to one study, curcumin considerably lessened postmenopausal women's hot flash frequency and intensity.
According to a different study, postmenopausal women who take curcumin plus soy isoflavones may experience less vaginal dryness.
Another scientific trial gave curcumin pills to hot flash-prone women for three months. Hot flash severity and frequency significantly decreased, and quality of life indicators was improved, according to the findings.
Similarly, to this, taking curcumin pills for eight weeks significantly improved mood and decreased depression symptoms in a clinical experiment involving women with menopausal symptoms.
Additionally, it has been demonstrated that curcumin works well to control menopausal-related weight gain. In a clinical study, the impact of curcumin on obese postmenopausal women was investigated.
The body mass index and waist circumference significantly decreased, according to the findings [9].
Human trials have also been carried out to examine the effectiveness of curcumin in treating the symptoms of menopause in addition to clinical trials.
In one study, the ability of curcumin to lessen menopausal-related joint pain was examined. The outcomes showed that curcumin may have therapeutic effects on menopausal-related joint pain.
Curcumin has shown promise in treating a variety of menopause symptoms.
Clinical and human investigations have revealed curcumin's enormous potential in easing menopause symptoms, from lowering hot flashes and joint pain to controlling mood swings and sadness [10].
Nevertheless, these trials have produced encouraging results that suggest curcumin might be a workable substitute for conventional pharmaceutical menopausal treatments. a healthy alternative that could greatly raise the standard of living for menopausal women.



Comments